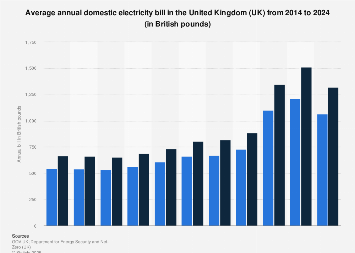
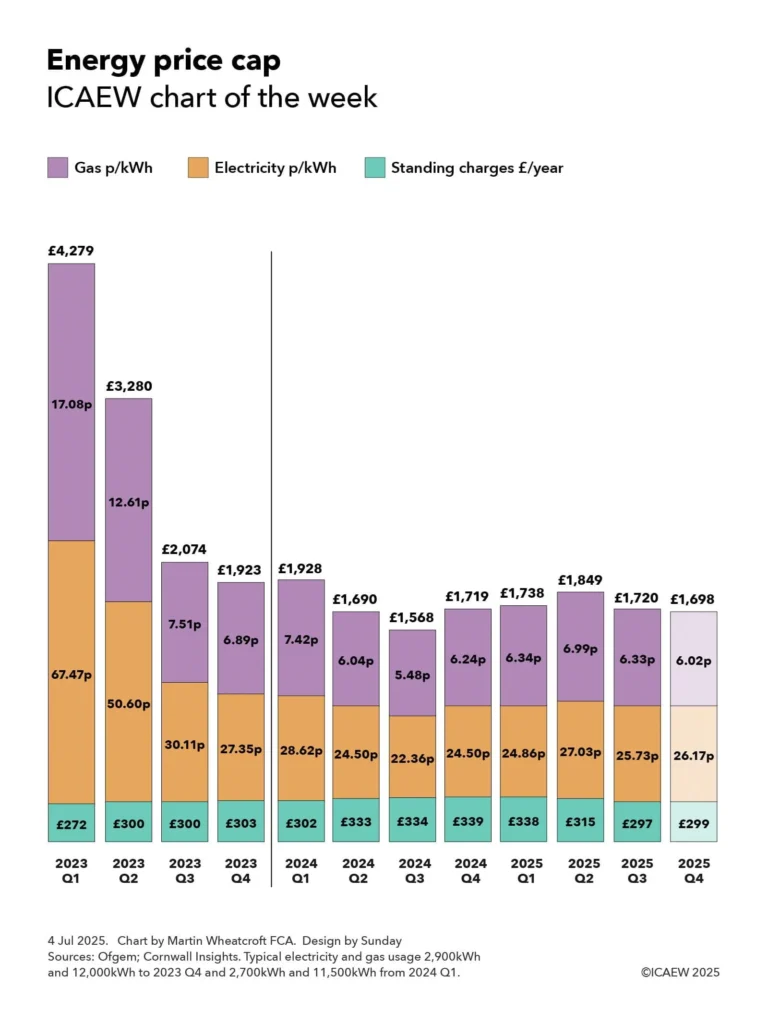
£108 Energy Hike Incoming: If you’re living in the UK, your energy bill is about to climb again — and not by just a few pounds. The energy regulator Ofgem has approved a sweeping £28 billion upgrade plan for the nation’s power and gas grid. It’s the largest infrastructure overhaul since the 1960s, and it’s designed to prepare Britain for an electric future powered by renewables. Here’s the catch: it’s not free. To fund this modernization, households will shoulder part of the cost. By 2031, the average home could see energy bills increase by around £108 per year, or roughly £9 per month. This might sound like another hit to your wallet — especially after years of record-high energy prices — but there’s more to the story. This move could actually save money and secure Britain’s power supply in the long run.
£108 Energy Hike Incoming
The £108 energy hike may not sound like good news, but it’s part of a necessary transformation. The £28 billion Ofgem grid upgrade is about building resilience, reliability, and readiness for a cleaner future. In the long run, this investment will reduce the risks of blackouts, improve energy security, and create jobs — all while helping the UK transition away from fossil fuels. It’s a bold move toward a smarter and more sustainable energy system. The best thing you can do? Get informed, stay efficient, and take advantage of government programs that help lower your energy use. The future of energy is changing — and this time, everyone has a role to play.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| What’s Happening | Ofgem approved a £28 billion plan to upgrade gas and electricity networks across the UK. |
| Impact on Households | Average bills will rise by £108 per year by 2031, or £9/month. |
| Why It’s Needed | The UK’s aging grid can’t support future demand from renewables, EVs, and electrified heating. |
| Who’s Behind It | The energy regulator Ofgem and major UK network operators (including National Grid). |
| Potential Savings Offset | Efficiency gains could cut the net rise to £30/year per household. |
| Official Source | Ofgem Press Release |
£108 Energy Hike Incoming: Why This £28 Billion Plan Matters
Britain’s power grid is outdated — much of it was built when home electricity needs were simpler. Today, millions of homes rely on high-energy devices, electric vehicles, smart tech, and heat pumps. Meanwhile, renewables like wind and solar are supplying a growing share of electricity — but that power has to be transported efficiently from where it’s generated (offshore wind farms in Scotland and the North Sea) to where people actually live.
Ofgem’s plan includes:
- Building new high-voltage transmission lines to handle renewable power.
- Reinforcing gas and electricity distribution networks to reduce outages.
- Installing smart monitoring systems that can predict and prevent failures.
- Increasing grid resilience against extreme weather and cyber threats.
It’s not just an investment in cables and substations — it’s a long-term strategy to make the energy system more reliable, sustainable, and cost-efficient.
How the £108 Energy Hike Incoming Will Hit Consumers?
| Network Type | 2024 Average Cost | 2031 Projected Cost | Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity network | £162/year | £222/year | +£60 |
| Gas network | £174/year | £222/year | +£48 |
| Total | £336/year | £444/year | +£108 |
That means, for the average household, a yearly bill of around £1,600 could edge closer to £1,700.
However, Ofgem estimates that increased reliability and reduced grid congestion will bring long-term savings. Once renewable generation becomes cheaper and more stable, some of those higher costs could be offset — potentially cutting the net increase to just £30 per year.
The Bigger Picture: Energy Independence and Security
This decision isn’t just about keeping the lights on — it’s about reducing the UK’s dependence on foreign energy. When gas prices spiked globally after 2022, British households felt the pain immediately. Investing in domestic power infrastructure helps insulate the economy from future market shocks.
By strengthening the grid, the UK can:
- Support its Net Zero 2050 commitments.
- Lower carbon emissions by connecting more renewable sources.
- Minimize imported gas dependence from volatile markets.
- Build energy security that protects both households and industries.
In Ofgem’s words: “A strong, modern grid isn’t just an environmental goal — it’s a national necessity.”
Learning from the U.S.: How Modernization Pays Off
The UK isn’t alone in this transition. The United States is undergoing a similar grid modernization wave under its Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which allocates over $65 billion for clean energy and transmission upgrades.
Just like the UK, the U.S. faced backlash over the short-term cost increases. But over time, these investments have reduced blackouts, improved reliability, and even created thousands of skilled jobs in renewable infrastructure and grid management.
The key lesson? Modernization costs upfront, but not modernizing costs far more in the long run — in outages, inefficiency, and environmental damage.
The Long-Term Benefits: Beyond the Bills
Upgrading the energy grid brings benefits that go beyond monthly bills. Here are a few examples that matter to consumers, professionals, and the planet:
- Fewer Outages and Power Cuts – A smarter, more distributed grid reacts faster and prevents blackouts before they happen.
- More Renewable Energy – The UK will be able to transmit offshore wind and solar power more effectively, cutting reliance on fossil fuels.
- More Jobs and Innovation – The investment is expected to create over 20,000 new jobs in engineering, maintenance, and data systems.
- Cleaner Energy Mix – Reducing carbon emissions from electricity generation will bring environmental and public health benefits.
- Economic Resilience – A stable grid lowers risk for businesses, industries, and investors.
Experts at Bloomberg and PwC estimate that efficient grid modernization could save the UK economy £10–£15 billion over two decades.
Practical Advice: How to Manage the £108 Energy Hike Incoming
Even though this rise is coming, there’s a lot you can do to reduce its impact.
1. Review Your Energy Use:
Go through your energy statements and identify trends. Apps like Loop Energy and EnergyHub provide visual breakdowns of usage by time and device.
2. Install a Smart Meter:
Smart meters are free and help track real-time usage, allowing you to shift consumption to off-peak hours when rates are lower.
3. Switch Tariffs or Providers:
Don’t assume your current supplier is the best deal.
4. Boost Home Efficiency:
Proper insulation, LED bulbs, and efficient heating can save hundreds each year.
5. Consider Renewables:
If you own your home, explore solar panels or home battery systems. The Smart Export Guarantee (SEG) lets you earn money by selling surplus power back to the grid.
6. Stay Updated:
Follow reliable sources like Ofgem, BBC Energy News, and Energy Saving Trust for updates.
Industry Impact and Future Outlook of £108 Energy Hike Incoming
The ripple effects of this £28 billion plan extend beyond homes.
For Businesses:
Small and medium enterprises will likely see minor increases in energy costs, but they’ll also gain from more reliable power — a big win for sectors dependent on continuous operation, such as tech, healthcare, and manufacturing.
For the Economy:
The investment is expected to stimulate green job growth and attract foreign capital in renewable energy projects. As grid bottlenecks ease, renewable developers can connect new projects faster, accelerating progress toward the Net Zero 2050 goal.
For Investors:
Funds focusing on infrastructure and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) portfolios are expected to see higher activity. Financial experts predict strong returns in smart energy management and grid automation sectors.